File Exchange
Import/export between Houdini and other 3D software
Overview
Houdini supports many file formats for exchanging assets with Cinema 4D, Blender, Unreal, Maya, and more. Choose formats based on data type, compatibility, and workflow.
Common File Types
- USD (.usd, .usda, .usdc, .usdz): Universal Scene Description—best for complex scenes, hierarchy, referencing. Widely used in VFX, animation, games.
- Alembic (.abc): Fast geometry/animation caches. Supported by most 3D apps.
- FBX (.fbx): Meshes, animation, cameras, lights. Common for games/DCC, but may have quirks.
- OBJ (.obj): Simple mesh format—geometry and UVs only.
- GLTF/GLB (.gltf, .glb): Modern format for real-time/web/AR. Supports meshes, materials, animation.
- STL (.stl): For 3D printing—geometry only.
- Other: BGEO (native), DAE (Collada), image sequences for textures/simulations.
Tips for Cross-Software Exchange
- Check compatibility and version for each format.
- Use USD for complex scenes/assets (Unreal, Maya, Blender).
- Alembic for baked geometry/animation.
- FBX for rigs, animation, cameras—test for quirks.
- OBJ for static meshes/UVs (not animation).
- GLTF/GLB for real-time/web workflows.
- Always check scale, orientation, axis after import/export.
- For textures/materials, verify format support or export separately.
Alembic Export Example
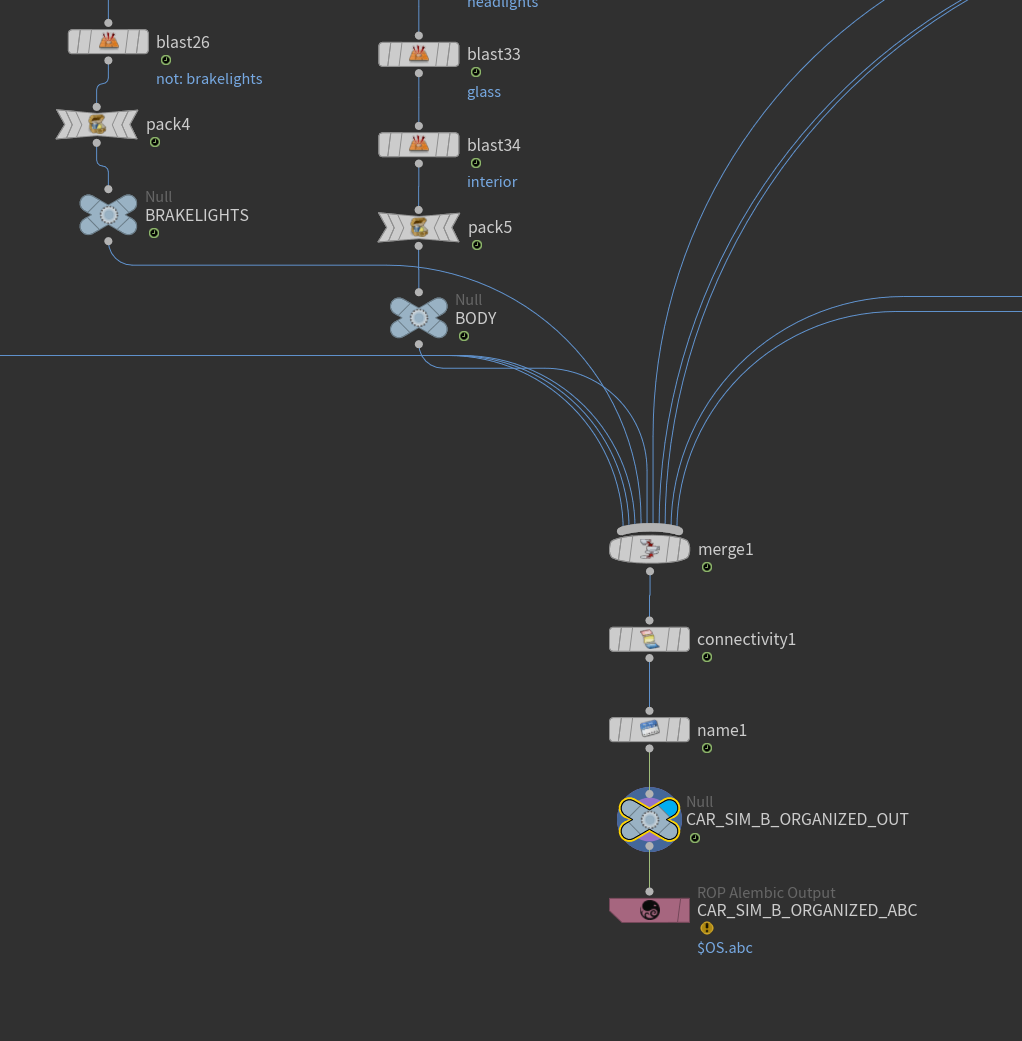
Packing & Export Workflow:
- Pack nodes group each component (e.g. brakelights, glass, body).
- Merge node combines all packed components.
- Connectivity node assigns unique IDs to each connected piece.
- Name node gives each component a unique class attribute.
- ROP Alembic Output exports the organized components as a single Alembic file.
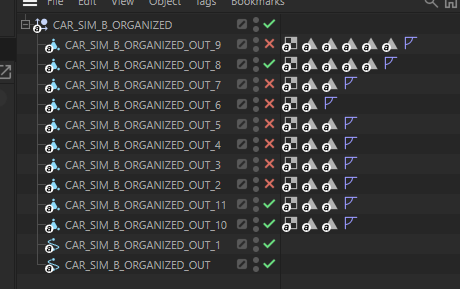
Result in Cinema 4D:
- Alembic file imports as a single object tree.
- Each component is listed separately and can be isolated or manipulated individually.
- This makes it easy to work with complex assets and maintain organization across software.