POP Solver Example Setup
Basic particle system setup using POP Solver in Houdini
Overview
The POP (Particle Operator) Solver in Houdini is a powerful system for creating and manipulating particle simulations. This example demonstrates a basic setup for particle emission and behavior control.
Node Network Structure
Preview of a POP solver simulation in action
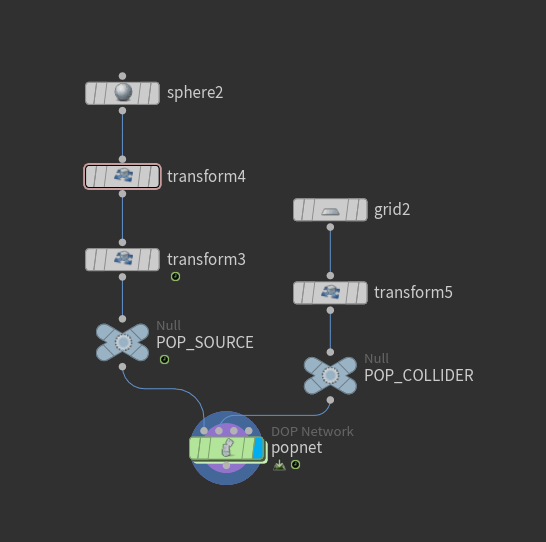
Overview of the POP network structure showing the main components
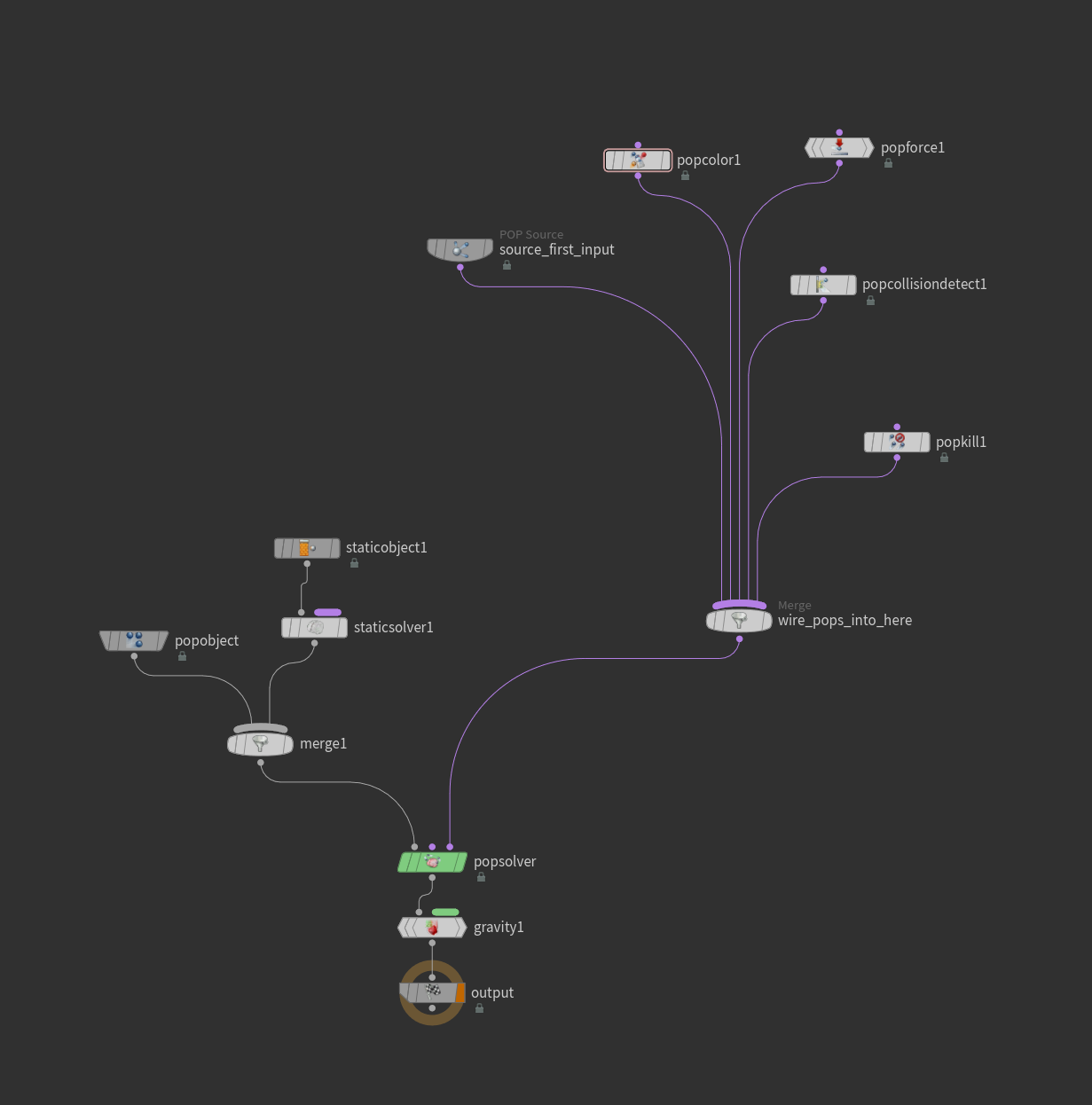
Detailed view of the POP solver setup and particle controls
Key Components:
- POP Source: Controls particle emission, including birth rate and initial attributes
- POP Force: Applies forces to the particles, such as gravity or wind
- POP Drag: Adds air resistance to create more realistic particle movement
- POP Group: Organizes particles into groups for targeted effects
Common Parameters
Essential Settings:
# POP Source Parameters
birthrate = 100
life = 2.5
impulse = 10
spread = 30
# POP Force Parameters
force = {0, -9.81, 0} # Standard gravity
amplitude = 1.0
# POP Drag Parameters
drag = 0.1
turbulence = 0.05Tips for Parameter Adjustment:
- Increase
birthratefor denser particle systems - Adjust
lifeto control how long particles exist - Use
spreadto control the emission cone angle - Balance
dragandturbulencefor natural movement
Best Practices
- Always use a
nullnode at the network output for clean organization - Cache heavy simulations to disk using a File Cache SOP
- Group particles early in the network for better control
- Add visualization nodes (such as Trail SOP) for debugging
- Use POP wrangler for custom particle behaviors